RESEARCH CASE STAUDY
Investigating Decision-Making and Barriers in Nutrition-Related Behaviours
The focus of this research is in the area of healthy nutritional habits. This research case study met the research aim through an extensive study of relevant literature, conducting in-depth interviews, diary studies, and analyzing data to gain insights.

Role:
Researcher
Methodology:
Semi-Structured User Interview
Survey
Expert Interview
Dairy Studies
Tool Used
Spreadsheets
Miro
Mural
Team & Timeline
Brooks, Kateryna
(sep-Dec 2022)
Research Journey
CHALLENGE
PROCESS
ANALYSIS
SYNTHESIS
NEXT STEPS
THE CHALLENGE
Adults in the Workforce often Struggle with Maintaining Healthy Nutritional Habits.
Studies have shown that the average office worker resorts to unhealthy eating options due to factors such as work circumstances and other personal responsibilities (Park, 2009). To better understand the key drivers behind this habit, this study will examine behaviours based on the constructs of the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB). This theory focuses on a person’s intention to engage in specific behaviours. The stronger the person’s intention is to perform a particular behaviour, the more effort they will exert to perform it. The intentions consist of three factors: attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control (Brookes, 2021). TPB is a well-researched model that has often been used as a reliable predictor of health-promoting behaviours and interventions (M.S. McDermott, 2015).
-
Attitudes
-
Subjective Norms
-
Perceived Behavioral control
THE PRIMARY PURPOSE
-
What support do people in the workforce need for educating themselves on healthy lifestyle
-
What key factors drive their intention and behaviour with their current eating habits?
-
What barriers might be preventing themfrom employing healthier habits?

PROCESS
Research Methodology
The study consisted of a pre-screener survey, 1 expert interview, 5 diary studies, and 5 in-depth follow-up interviews. The pre-screener was conducted informally to recruit 5 diary study participants who are working adults between the ages of 25-45 and interested in improving their nutritional habits.
Why
Diary Study:
-
To track variables that change over time such as:
-
how busy their day was
-
their motivations, barriers, moods, and food choices
-
Conducted over 3 days
In-depth interview
-
To better assess the individual’s perceptions and beliefs
Asked about their daily life, past and current nutritional behavior, motivators, and intentions
ANALYSIS
Coding
Interviews and diaries were coded to identify the themes related to the research questions based on the Theory of Planned Behaviour. The codes were primarily divided into three factors;
Attitudes
Subjective norms
Perceived behavioral control
.png)
SYNTHESIS
Affinity Diagram
We grouped each contributing factor under positive and negative influence and counted how many times it was mentioned to understand its importance. Each factor then themed using a similar methods to the coding system. Attitude had the most positive influencing factors while perceived behavioral control had the most negative influencing factors.
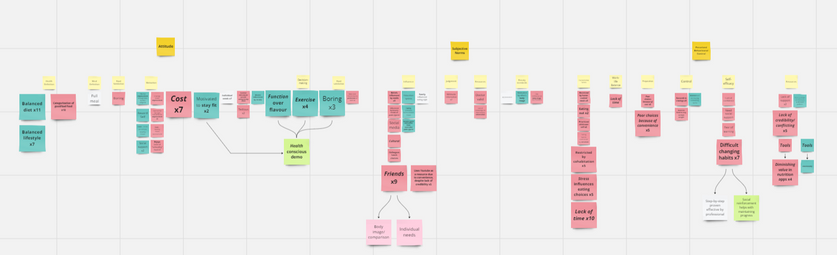
Modified Groupings
We further regrouped our insights into categories that helped us create actionable insights by creating slightly different sub- categories:
-
Drivers for positive behaviors
-
Barriers
-
Tools that works
-
Tools that don't work
Internal Motivators:
-
Drivers for positive behaviors: Desire to be healthy
-
Barriers: Time, Ease, Cost, Pleasure, Utility
-
Helpful Tools: simplicity, simple healthy recipes

External Motivators:
-
Drivers for positive behavior:
Motivation by other's success, culture
-
Barriers:
Negative influence from friends and colleagues
,beauty standards, family, or cultural expectations.
-
Helpful Tools:
Having rapport with a coach , building a support system with friends and family

INSIGHTS
Things We Uncovered
After synthesizing the content gathered from the semi-structured interviews, Survey and Dairy Studies, we uncovered valuable insights that shed light on our research questions.
Here are few insights:
INSIGHTS
Attitude
Most participants wants to buy a healthy food, but they are swayed by low-cost offers that are less nutritious.
Three of participants who exercise wants to eat protein- balanced and healthy meals, because they want to stay fit and build muscle, but they find the taste of healthy food to be boring .



INSIGHTS
Subjective Norms
Four participants want to conform to certain body standards, because of the influence from their friends and their beliefs on beauty, but the standards do not apply to everyone's individual body.
INSIGHTS
Perceived Behavioral Control
Almost all participants want to have a quick and easy meal, because they don't have time, but it makes them pick unhealthy meal choices due to convenience.
Nutritionists who work with clients to help them to eat healthy find that it helps their clients to break down tasks into baby steps, because it makes the process of eating healthy manageable and less overwhelming, but they need to give praise and provide social support to help the behavior stick.


Recommendations
-
Help users be intentional, encourage sustainable progress by applying small step- by step goals
-
In-the-moment accountability; provide a platform for on-the-go motivation when needed, offer a easy to share goals and progress with loved ones for social support
-
Connect users to professionals for credible information and nutrition programs built for their individual needs
NEXT STEPS
Future Research
-
What tools do coaches currently use?
-
What tools would help better connects coaches to users?
-
How do users feel about sharing their progress socially?
-
Are there any competitor tools that offer similar features?